Since Linus Torvalds announced that the Linux kernel project was complete and ready for use, developers have exploited this treasure that was buried in Bell Labs, the preserve of universities, the military, and major companies. He has been working on it for a long time. He took advantage of the readiness of the Torvalds kernel and its alignment with his ideas that he and his team are working on. They supported the kernel with free and open source tools and programs, and what is called GNU/Linux appeared.
Subsequently, projects led by passionate and enthusiastic about this new baby emerged. They improved these additions and modified them to suit their trends and visions, and the projects KDE and Gnome became public.
Big tech companies like RedHat and Novell invested their expertise and money into the market with Linux-based operating systems and FOSS and built their own public distributions.
What do we mean by linux distribution?
Simply put, the distribution is the Linux operating system, consisting of the kernel that performs the hardware recognition function, in addition to the tools that the user works on such as the desktop interface, package manager, psoriasis, image editor, text editor and others. Distributions differ according to their supporters and those behind them. Companies or the technical community and their trends, so we find this momentum and the huge amount of distributions that appear and then disappear with the disappearance of their owners for one reason or another, or the lack of financial support for companies.
parent distributions
These are the distributions that appeared with the emergence of Linux and created its philosophy, then came new distributions that were built on the corners of the parent distributions, we call them the daughter distributions (they are just names to understand the idea of the topic).
Slackware distro
The first distribution to appear is the Slackware distribution, and that was in 1993 by Patrick Volkerding. The distribution was derived from another distribution that did not survive, called SLS, which is an abbreviation for (Softlanding Linux System), and Patrick adopted simplicity in building this The distro is intended mainly for professionals who know their way to Linux, everything in it is built manually, meaning that whoever uses this distro will be his friend on the command line.
slackware 14.2
Slackware review
Dozens of distros have adopted the Slackware philosophy as a base for development and construction, for example the ancient SUSE and the beautiful, light Slax (currently built from Debian).
Debian distro
The second distribution to appear is Debian, which is one of the oldest, most well-known and stable distributions, and the mother of hundreds of distributions that are generated every day. The Debian project is a free enterprise with a strong community of developers and programmers, and it has a very strict policy of accepting packages and pushing them into their repositories; Therefore, it is one of the most stable and secure distros. The first stable version of Debian appeared in 1996, while the unstable version began working on it in 1993, three years of work and testing until they reached a stable version.
Debian
Among the most important distributions that were built from Debian, the famous Ubuntu distribution, which is credited with introducing people to Linux and removing the aura of terror and fear of using it. This new and beautiful system, and thus Linux has become popular among people and those who use it are proud of that after it was the preserve of hackers and technology geeks. In addition to Obono, we find the Knoppix distribution that still silently maintains its principle of using Linux live from a CD, DVD or USB flash drive.
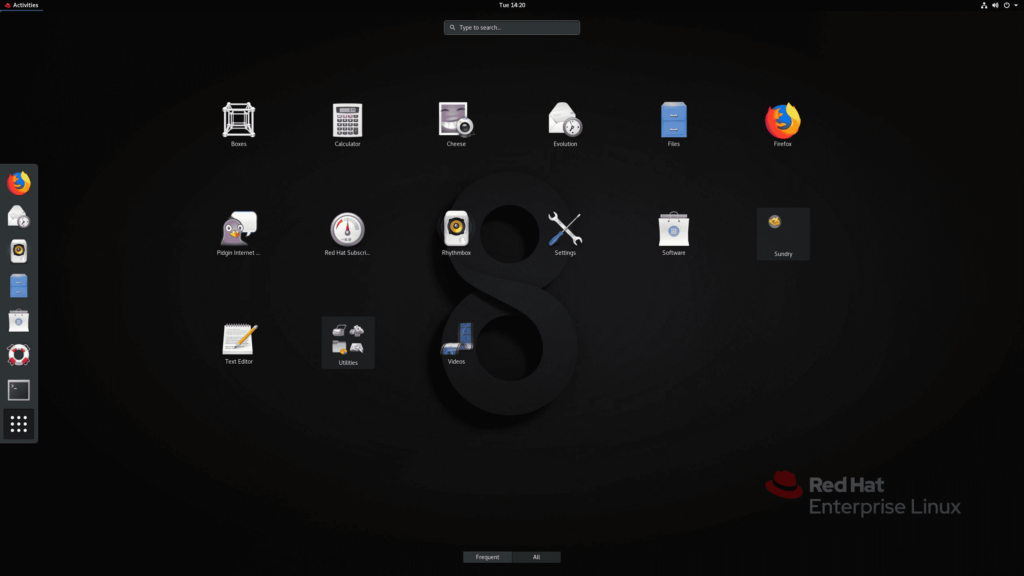
Red Hat Distribution
The third distribution to appear is the Red Hat distribution, and the name is taken from the name of the company that supports and sponsors this distribution, which benefited from Linux and free open source software and made good use of it, and in return it provided a lot to this free world. (Gnome), the free office suite (LibreOffice), Windows (Xorg) and several other projects are among the pillars of free software.
One of the most important distributions that were built from the beautiful distribution Fedora, which is the largest of the projects supported and sponsored by Red Hat, and the distribution that has been rebuilt the Red Hat distribution again in the form of a distribution directed to enterprises and businesses called (RHEL), in addition to the Centos distribution (CentOS) is also business-oriented; But for free, unlike (RHEL), which provides its services for a fee.
Another red hat distro that did a lot for free software and one of the first distros that made Linux less accessible and enticed people to use it is Mandrake; But it suffered a lot due to the lack of support and stopped publishing several times, but the enthusiastic and loving community revived it again under the name of Mandriva, which stopped again and the project is now turned into the Mageia distribution.
These are the distros from which most of today’s distros have sprung in one way or another, and they are credited with making Linux today.